| Grant number | AHRC (No. 30794) |
| Funded by | Cultural Heritage and Development in Egypt (AHRC), the Science and Technology Development Fund (STDF), Egypt. |
| Beneficiary | Cairo University Faculty of Engineering |
| Date | 2019 - 2021 |
| Budget | 80,528 Pounds Sterling for Egypt side |
Summary:
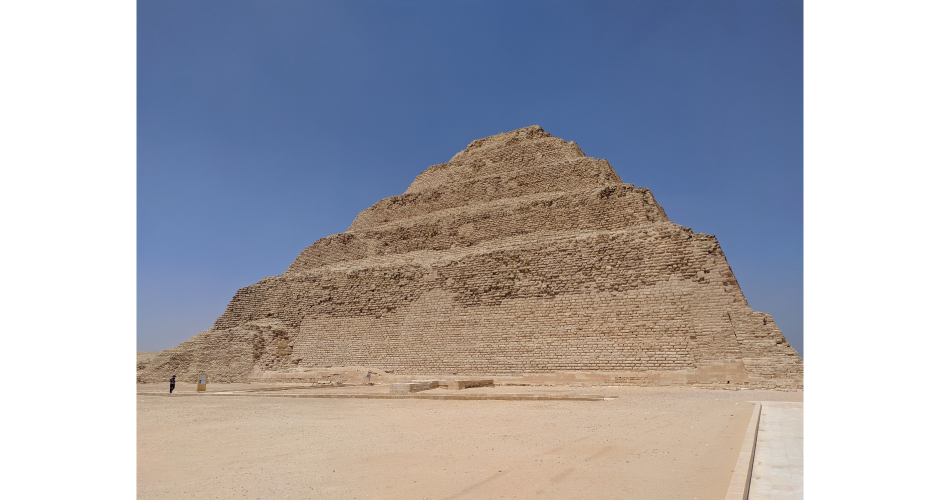
The historical sites and monuments in Egypt are among the most important in the world and conserving this heritage is crucial. The large damage observed in hundreds of monuments after the Cairo Earthquake in 1992 unveiled the fragility of the Egyptian heritage asset to seismic hazards. More than 12 years and a huge investment were needed to reopen some of the damaged sites. Unfortunately, the current knowledge on the strengthening and mitigation of the seismic risk in heritage buildings is focused on invasive solutions that require the alteration of the historical structure and, with it, the modification of its essence. In addition, these precursor works are not focused on the specific case of the Egyptian monuments and the seismic activity in the region. As a result, the cultural asset of Egypt is threatened by the seismic hazard.
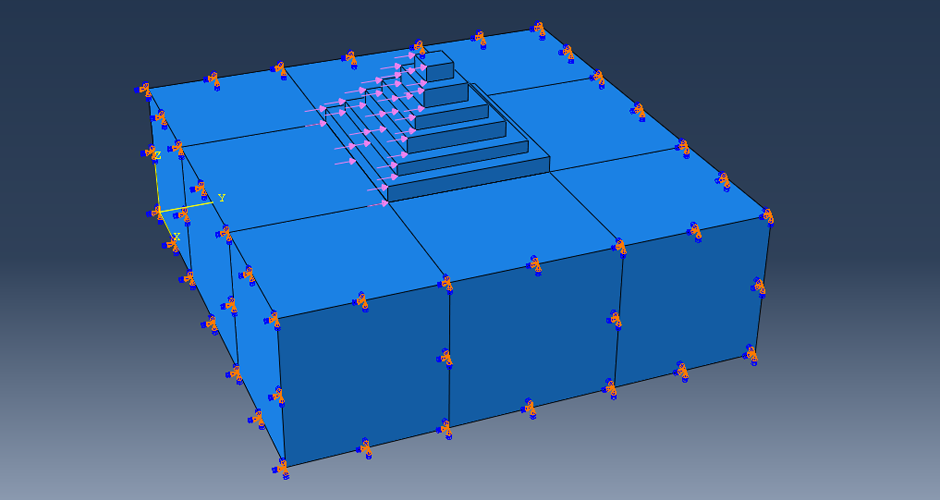
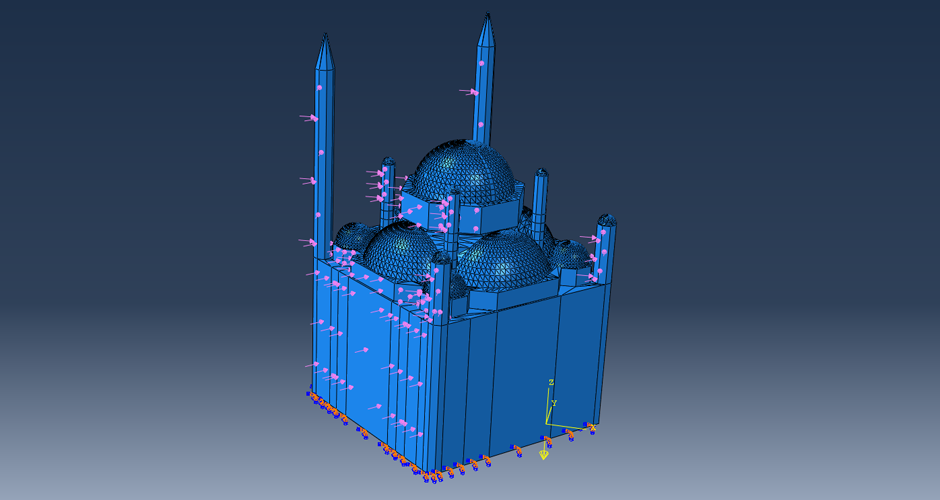
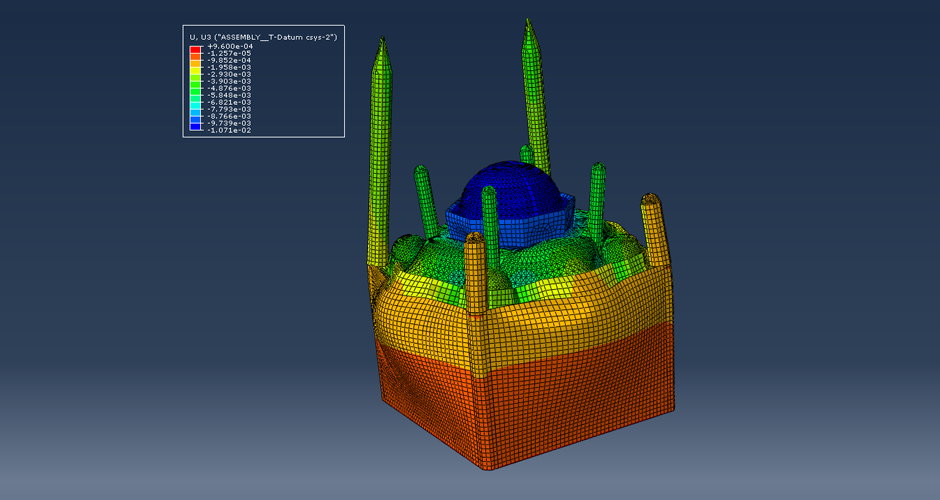
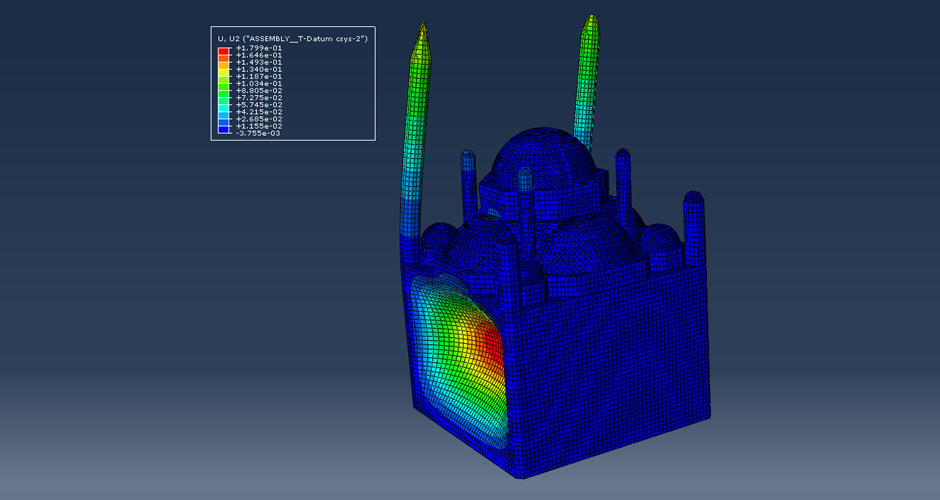
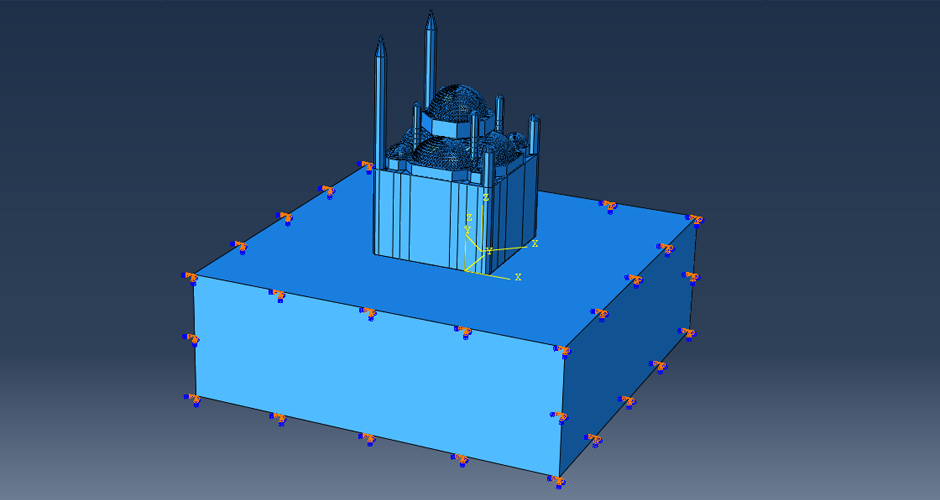
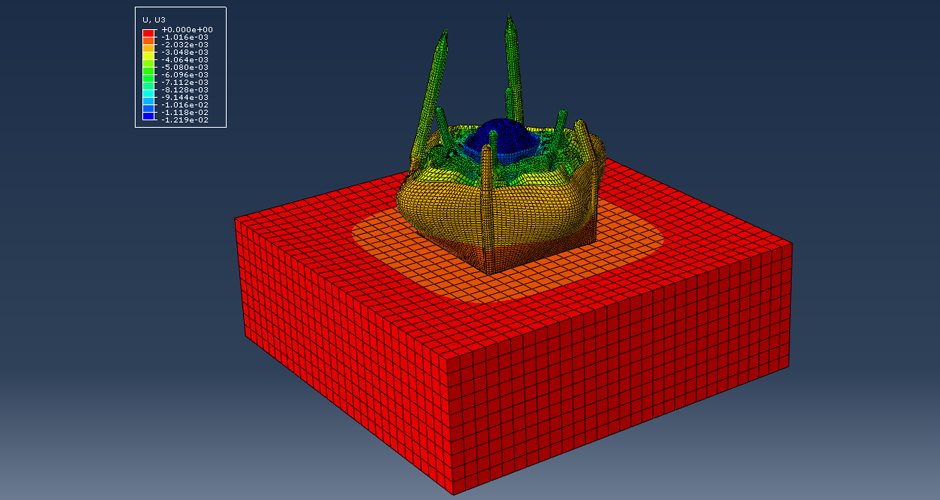
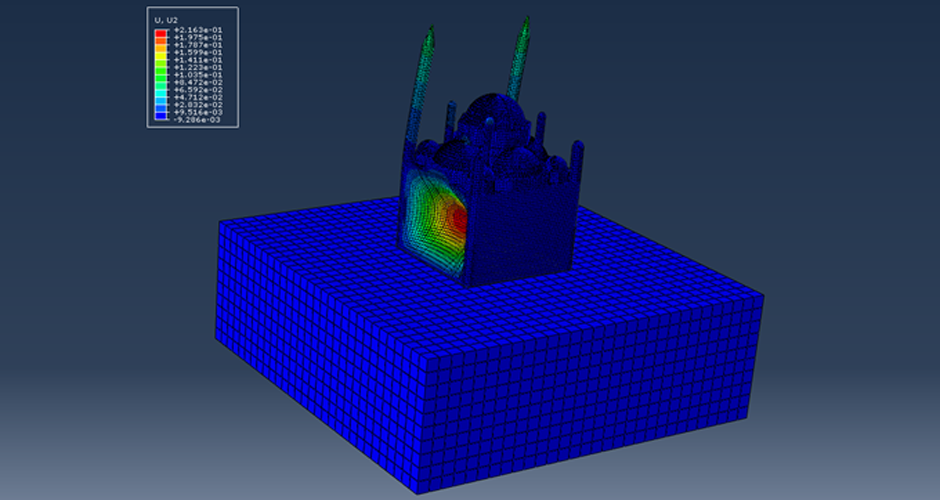
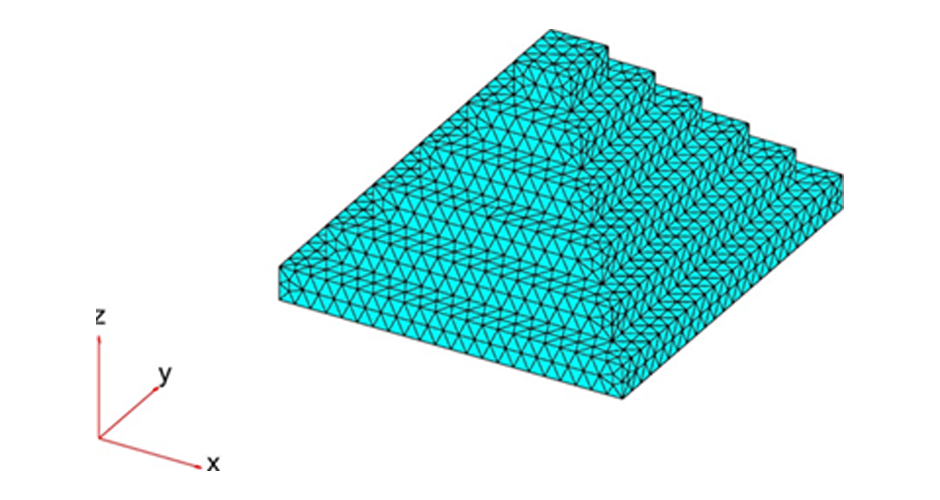
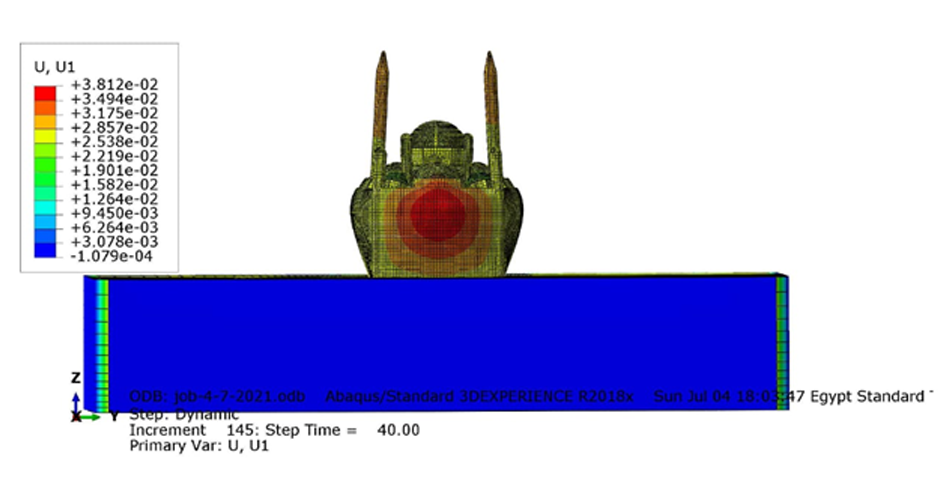
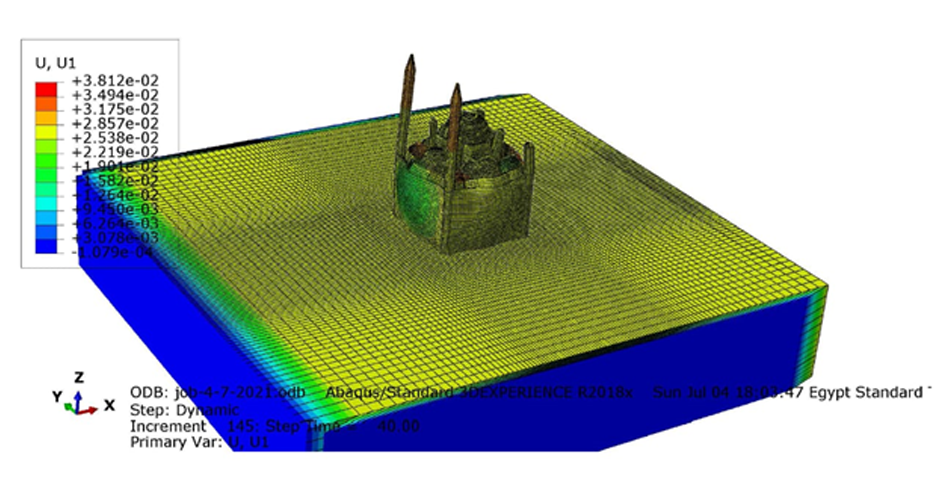
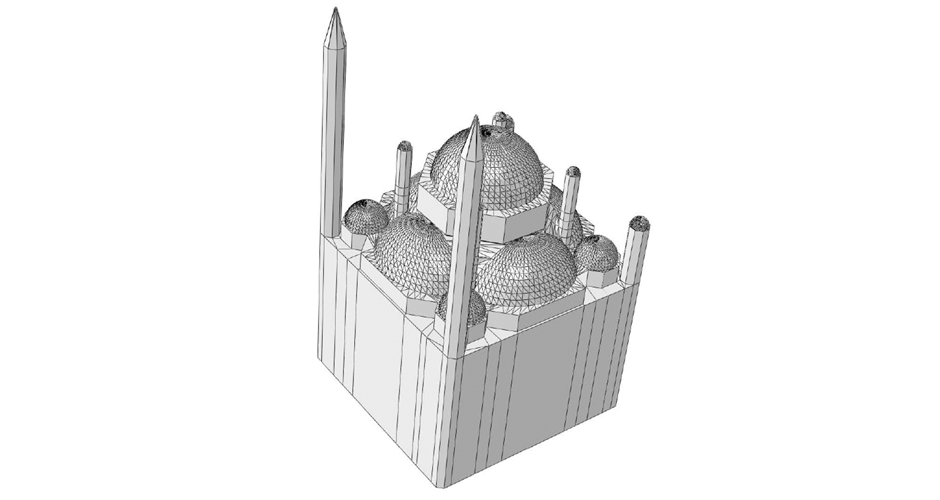
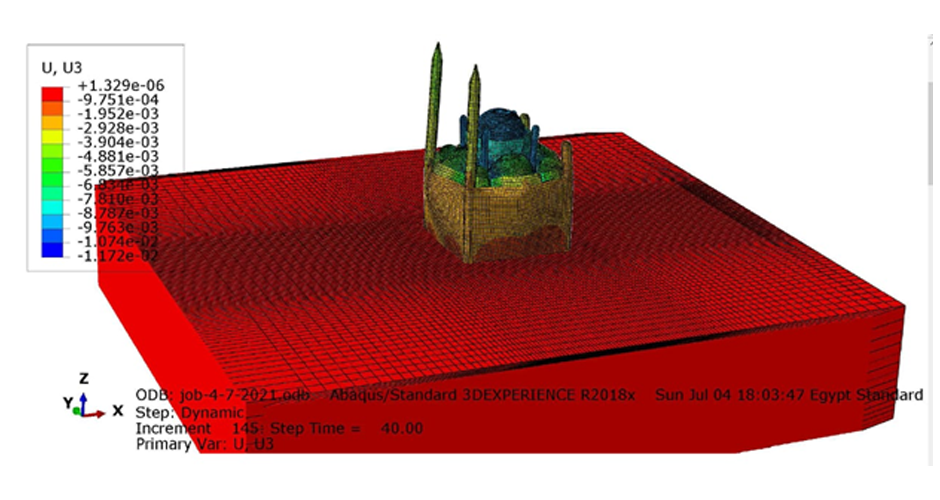
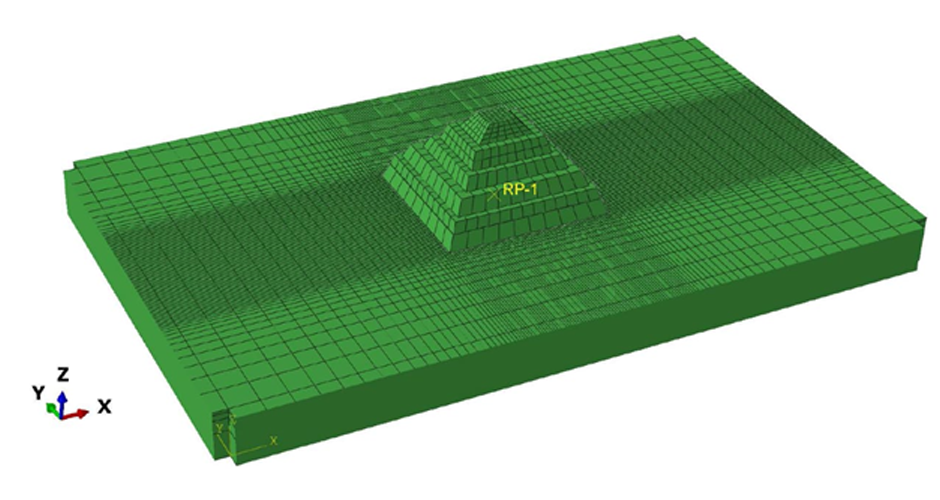
This research aims to apply an innovative concept in earthquake engineering to the control of whole heritage sites without the need for alteration in the ancient structures. The idea is to introduce a vibrating barrier (ViBa) in the ground (completely external to the protected structures) that is able to interact with the soil and the earthquake in order to mitigate the seismic risk in the entire site. The project combines the expertise of academic teams in Egypt and UK towards the application of this novel idea. The team at Cairo University will implement an advanced numerical technique with Boundary Elements to solve the soil-structure interaction problem with ViBa. This barrier will be designed and tested experimentally in scaled models by the team at the University of Brighton, the original developers of the ViBa. Finally, the expertise of the team at City, University of London, in nonlinear dynamic analyses will be applied to the study of the site with the ViBa in large Finite Element models that consider the particular seismic, geotechnical and structural conditions in Egypt. The successful development of this project will result in the generation of new and fundamental knowledge on the control of structures with protection barriers, ultimately preserving the Egyptian heritage and the lives of the persons in these sites. It will also result in the development of design guidelines that will facilitate the application of the project outcomes by engineering practitioners and industry.
Impact:
The study proposes the use of the innovative Vibrating Barrier (ViBa) system for preservation of Egypt's cultural heritage structures against seismic risk. Egypt's tourism relies heavily on its ancient historic structures, and protecting them from earthquake attacks is a priority for the country, in particular that damage was observed in hundreds of monuments after the devastating Cairo earthquake in 1992. The adoption of the ViBa system is particularly suited for historic structures as it does not require any alteration of their shape or image.
The impacts of the proposed study can be summarized as follow:
1- The proposed study will result in much safer cultural heritage structures when subjected to strong earthquake excitations.
2- The outcome of the study is a detailed guideline for preservation of cultural heritage structures to be presented to the local authorities in Egypt.
3- The study will provide an opportunity for several young engineers and researchers to be involved in state-of-the-art research in the field of seismic control and preservation of archaeological buildings.
4- Many other stakeholders will benefit from the research outcomes, such as researchers working in the field of Conservation of Architectural Heritage and Computational Structural Analysis, as well as government professionals in the Ministries of Antiquities, Tourism, and Scientific Research.
5- The research team will benefit from the exciting new concept of the ViBa to recruit pre-university students to the field of Engineering and Archaeology.
6- The results of the proposed research will be disseminated to the public through different publications in technical and non-technical journals, presentations at different conferences, and at a Workshop organized by the research team to be attended by various stakeholders.
List of published papers:
Acknowledgement financial support (AHRC 30794):
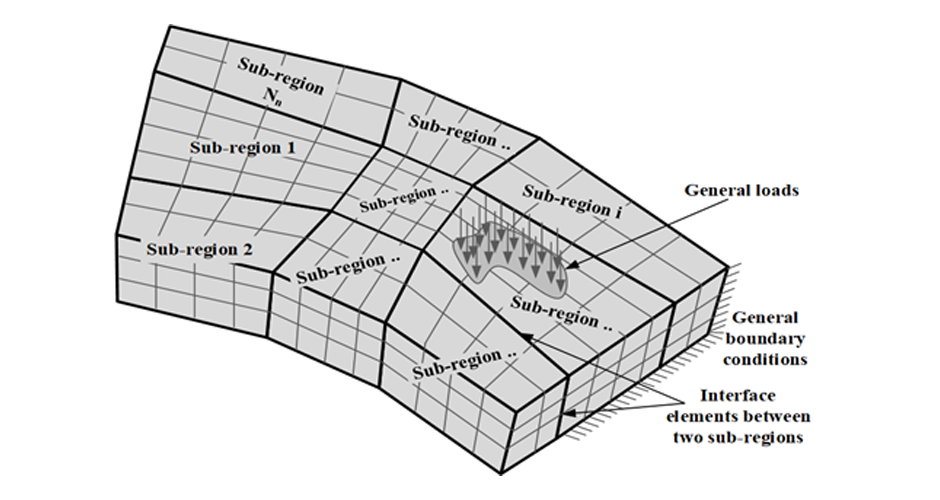
1-Azzam EOA, Farid AF, Rashed YF, and Elghazaly HA. "Stiffness-based multi-region 3d boundary element modelling of non-homogeneous soil", Journal of Engineering and Applied Sciences, Vol. 67, No. 4, pp. 867-884, 2020.
2-Farid AF, Elgalad MM, and Rashed YF. "Time period calculations for tall buildings on piled - rafts including soil-structure interaction effects ", Journal of Engineering and Applied Sciences, Vol. 67, No. 6, 2020.
3-Azzam EOA, Farid AF, Rashed YF, and Elghazaly HA. "The use of out-of-core iterative solvers for large 3D soil problems", Eng. Anal. Boundary Elem., Vol. 118, pp. 124-142, 2020.
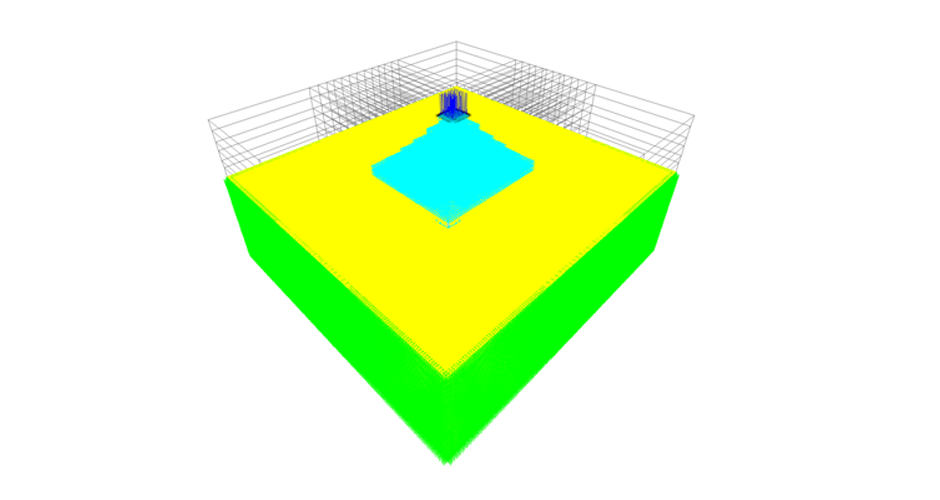
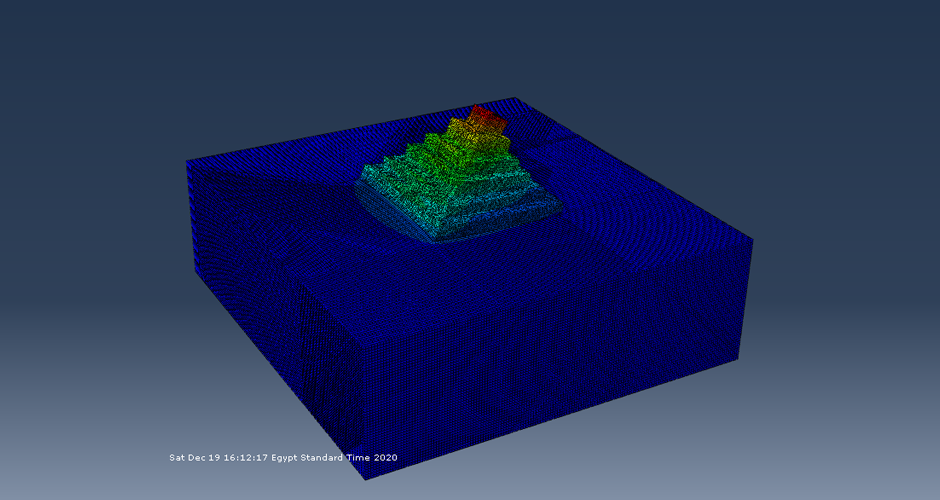
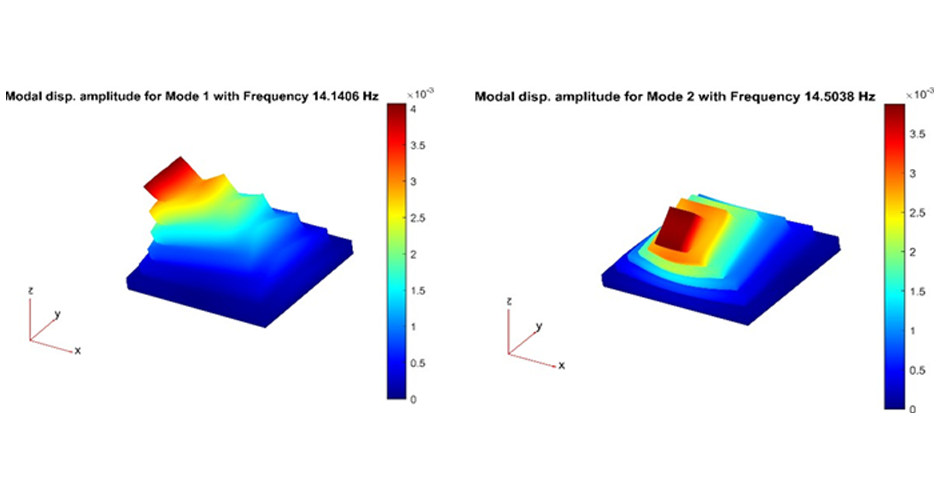
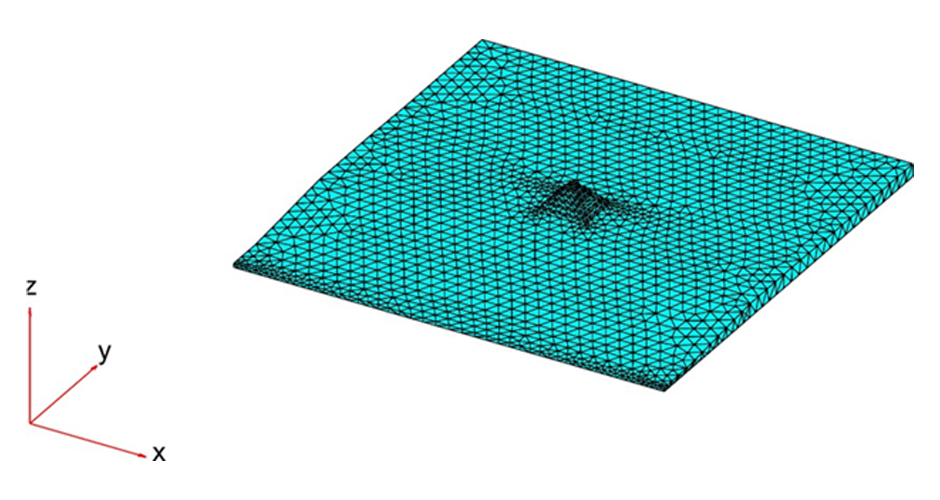
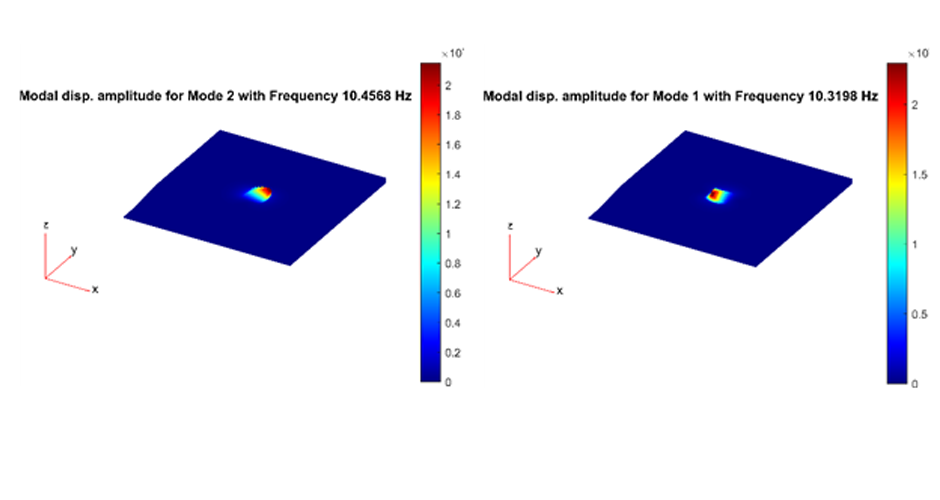
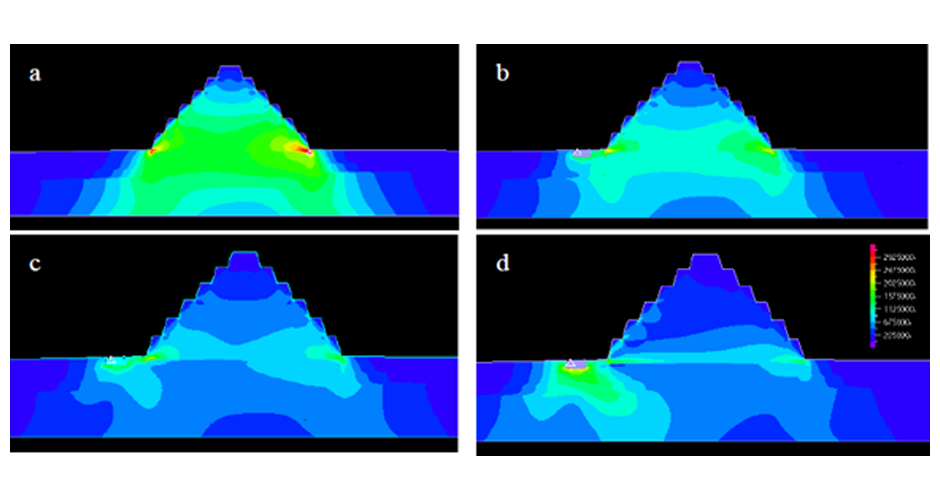
4-M. Shadlou, P. Cacciola, A. Ayoub, Y.F. Rashed and A. Tombari. "NON-INVASIVE VIBRATING CONTROL OF THE ZOSER PYRAMID", 8th ECCOMAS Thematic Conference on Computational Methods in Structural Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, Streamed from Athens, Greece, 27–30 June 2021.
Acknowledgement computer facilities support:
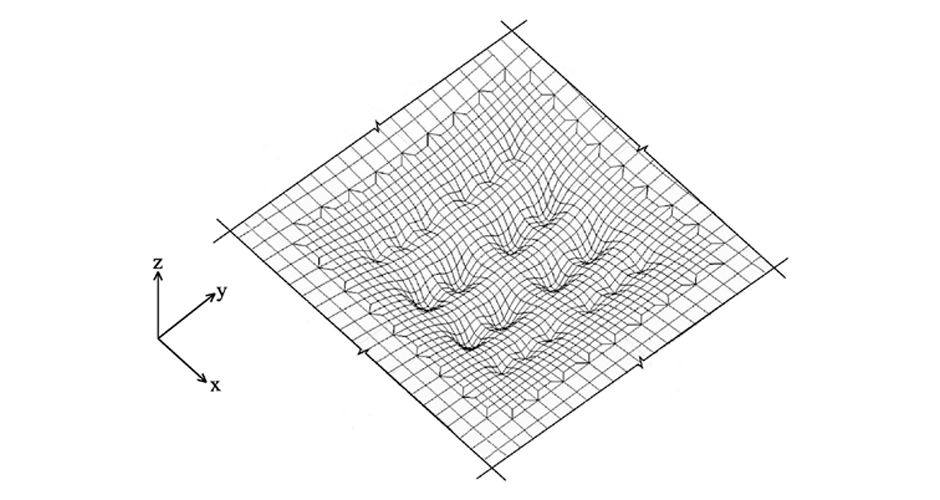
1-Elsheikh EM, Naga THA, Rashed YF. “Assessment of variational fundamental solution based elements in plate bending dynamics”, Engineering Analysis with Boundary Elements, Vol. 122, pp. 85-101, 2021.
2-Kamal MA, Farid AF, Rashed YF, Damage modeling using Eshelby inclusions, International Journal of Fracture, Vol. 229, pp. 95-111, 2021.
3- Kamal MA, Farid AF, Rashed YF, Explicit boundary element modeling of nonlocal damage with Eshelby theory, Engineering Analysis with Boundary Elements, Vol. 131, pp. 64-75, 2021.
Information
- Duration: 2 years